Facebook Twitter (X) Instagram Somali Magazine - People's Magazine
“In the realm of health, time is the most precious currency.” This sentiment resonates deeply in the Somali context, where access to timely medical care can significantly impact patient outcomes. As Somalia continues to rebuild its healthcare infrastructure, understanding complex medical conditions like pulmonary embolism (PE) is vital. PE is a leading cause of morbidity and mortality globally, and its timely diagnosis is essential, especially in a region where healthcare resources are limited. This article aims to highlight the crucial role of imaging in diagnosing and managing pulmonary embolism, providing Somali readers with insights into how these technologies can save lives and improve health outcomes in their communities.
The Role of Imaging
1. Diagnosis of Pulmonary Diseases
Chest X-Ray: A primary tool for initial evaluation, chest X-rays help identify conditions like pneumonia, pleural effusion, lung tumors, and tuberculosis. They provide a quick overview of lung structures and can reveal abnormalities in the lungs and surrounding tissues.
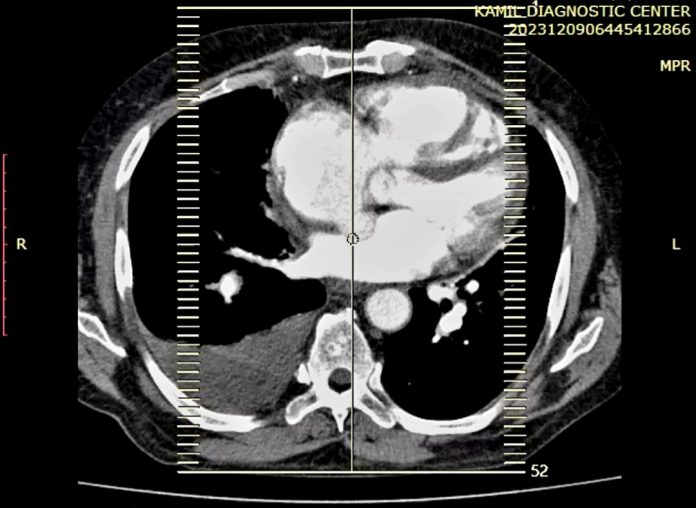
CT Scan: High-resolution CT scans offer detailed cross-sectional images of the lungs, making it easier to detect small nodules, interstitial lung disease, and emphysema. They are also invaluable in diagnosing pulmonary embolisms.
2. Staging of Lung Cancer
Imaging is critical in determining the extent of lung cancer. CT scans help assess the size and spread of tumors, while PET scans can identify metastatic disease. Accurate staging guides treatment planning and prognosis.
3. Guiding Interventional Procedures
CT and Ultrasound: Imaging modalities guide procedures such as biopsies and drainage of pleural effusions. For instance, CT can help target lung nodules for biopsy, ensuring accurate sampling.
4. Monitoring Disease Progression
Regular imaging allows for the assessment of disease progression or response to treatment in chronic conditions like COPD or interstitial lung disease. Changes in imaging can indicate the need for adjustments in management.
5. Assessment of Pulmonary Function
CT Pulmonary Angiography: This specialized CT scan evaluates blood vessels in the lungs and is critical in diagnosing pulmonary embolism. It provides detailed images of blood flow, helping assess vascular health.
6. Evaluating Complications
Imaging helps detect complications arising from pulmonary diseases, such as infections, abscesses, or pleural complications. Early identification through imaging can significantly impact patient outcomes.
7. Research and Clinical Trials
Imaging plays a significant role in pulmonary research, including the study of new treatments and disease mechanisms. Advanced imaging techniques, like functional MRI, help researchers understand lung function and structure in more detail.
8. Preoperative Assessment
Imaging is essential in preoperative evaluations for patients undergoing thoracic surgery. It helps assess lung anatomy, identify any underlying issues, and evaluate pulmonary function, which is crucial for surgical planning.
9. Evaluation of Extrathoracic Conditions
Conditions outside the lungs, such as heart disease or lymphadenopathy, can impact pulmonary health. Imaging assists in evaluating these conditions, helping to provide a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s health.
10. Educating Patients
Imaging findings can be visually communicated to patients, aiding in their understanding of their conditions. This can enhance patient compliance and involvement in their treatment plans.
In Somalia, the role of imaging in pulmonary health is increasingly vital, yet the country faces significant challenges in its healthcare landscape. With limited access to advanced imaging technologies due to under-resourced facilities, many regions struggle to diagnose and manage prevalent respiratory diseases like tuberculosis and COPD. Factors such as environmental exposure and ongoing conflict exacerbate these health issues, making early diagnosis crucial.
To address these challenges, there is a growing focus on portable imaging technologies, such as ultrasound, which can be used in remote areas. Training healthcare professionals in radiology and imaging techniques is essential to improve diagnostic capabilities. Public health initiatives supported by national and international organizations aim to enhance early detection and treatment of respiratory conditions.
Moreover, the instability in the region complicates efforts to establish and maintain imaging services. Research and data collection on respiratory diseases are limited, highlighting the need for improved imaging facilities to inform health policies. Community education about the importance of early diagnosis can foster greater awareness and encourage individuals to seek care.
Collaborations with international health organizations can bring much-needed resources and expertise, while telemedicine offers a potential solution for remote consultations, allowing for better access to specialist care.
In summary, while Somalia’s healthcare system faces considerable obstacles in utilizing imaging for pulmonary health, targeted efforts in training, technology, and partnerships can significantly improve health outcomes for its population.
Exploring Imaging Technologies
Imaging technologies, particularly Computed Tomography Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA), have revolutionized the diagnosis of PE. This non-invasive procedure allows for rapid visualization of the pulmonary arteries, making it an invaluable tool in emergency care settings. Key players in this field include local hospitals and international NGOs working to improve healthcare infrastructure. Initiatives like the Somali Health Initiative have made strides in increasing access to advanced imaging technologies, training healthcare workers, and raising awareness about PE. Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Limited access to trained radiologists, financial constraints, and the ongoing security situation can hinder the implementation of effective imaging solutions. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration within the healthcare sector.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Healthcare in Somalia
The future of imaging technology in Somalia holds great promise. As the country continues to integrate with the East African region, there is potential for shared resources and knowledge that could enhance the capacity to diagnose and treat PE effectively. Policy changes, such as increased investment in healthcare infrastructure and international partnerships, could significantly influence Somalia’s progress. Global trends toward telemedicine and remote diagnostics may also provide innovative solutions to the challenges faced in rural areas. For individuals, families, and communities, understanding the role of imaging in healthcare can lead to proactive engagement in health matters. Simple awareness of symptoms related to PE can encourage timely medical visits, which can ultimately save lives.
Conclusion
The role of imaging in diagnosing and managing pulmonary embolism is critical, especially in Somalia, where access to healthcare is often limited. By improving diagnostic capabilities, we can enhance patient outcomes and promote healthier communities. Somali readers are encouraged to advocate for improved healthcare services, participate in local health initiatives, and educate themselves and others about the importance of timely medical care and diagnostic technologies.